Setup GitFlow to run automated task
GitHub Actions help in integrating CI/CD so you can test, build, deploy your code right from GitHub. In this post, we will set up a couple of workflows to run when a PR is raised to any branch.
List of workflows:
- setup automated testing
- setup to validate build status
- setup to validate Docker build status
A simple workflow
A workflow is very easy to understand. It has a name attribute, on attribute and a list of jobsto be performed when an event matches the on attributes.
name: <workflow name>
on:
<conditions>
jobs:
job1:
...
steps:
...
job2:
...
steps:
...
We will get to Learn more about it when we'll set up an actual workflow.
1. setup automated testing
Like the simple workflow, we'll use the same structure here as well. Let's give it a name.
name: Test
The next step is when to trigger this workflow.
on:
# Run tests for push event in master branch.
push:
branches: [master]
# Run tests for any PRs.
pull_request:
This will match with any PR raised against any branch and any push event against the master branch. The same branch filter can be added to the pull_request part to run the GitFlow for any PR against the master branch.
Now, let's set up the job to perform when the GitFlow is triggered.
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Use Node.js to test
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
with:
node-version: '10.x'
- run: npm i
- run: npm test
env:
CI: true
The above snippet has only one job listed i.e test.
The job needs a machine to run on, which is specified using runs-on label. Other available labels are windows-latest, macos-latest.
steps section has a list of statements to execute.
-
uses: actions/checkout@v2check out the codebase: This action checks-out your repository, so your workflow can access it. -
uses: actions/setup-node@v1setup nodejs: Download and cache a version of node.js - npm by version specified (mentioned in with block). -
run: npm iandrun: npm testrun command: Runs command-line programs using the operating system's shell. The command can be of a single line or multi-line command.- single-line command:
run: npm install- multi-line command:
name: Clean install and build run: | npm ci npm run buildAn optional name attribute can be used to display step name or it defaults to the text specified in the
runcommand. Also, an environment variable CI needs to be set explicitly.
The final file looks something like this.
name: Test
on:
# Run tests for push event in master branch.
push:
branches: [master]
# Run tests for any PRs.
pull_request:
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Use Node.js to test
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
with:
node-version: '10.x'
- run: npm i
- run: npm test
env:
CI: true
2. setup to validate build status
The GitFlow file to validate build status is the same as the test one. The only thing needs to be updated in the file is the run command.
name: Test
on:
# Run tests for push event in master branch.
push:
branches: [master]
# Run tests for any PRs.
pull_request:
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Use Node.js to test
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
with:
node-version: '10.x'
- run: npm i
# the command for building the package
- run: npm run build
env:
CI: true
3. setup to validate Docker build status
The GitFlow file to validate Docker build status is also the same as the test one. The only thing needs to be updated in the file is the run command. If you have a docker-compose.test.yml or Dockerfile in the root directory, then it'll build the docker image. It will just build the image and not upload it to any container registry.
name: DockerBuildTest
on:
push:
# Publish `master` as Docker `latest` image.
branches:
- master
# Publish `v1.2.3` tags as releases.
tag:
- v*
# Run tests for any PRs.
pull_request:
jobs:
# Run tests.
# See also https://docs.docker.com/docker-hub/builds/automated-testing/
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Run tests
run: |
if [ -f docker-compose.test.yml ]; then
docker-compose --file docker-compose.test.yml build
docker-compose --file docker-compose.test.yml run sut
else
docker build . --file Dockerfile
fi
What's next
The same .yml file can be updated to upload to a registry with a successful test job.
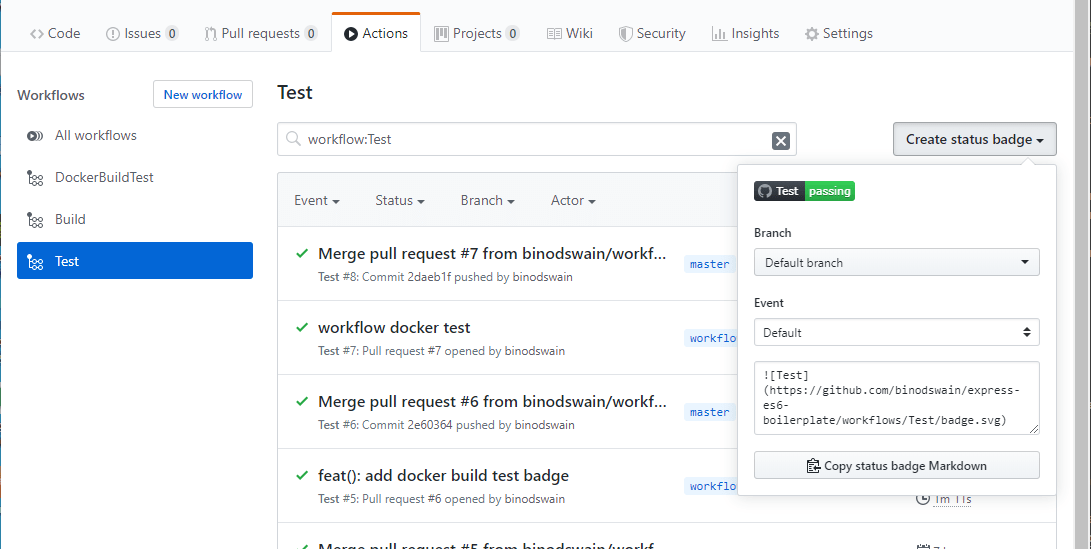
The status of the task can be displayed as a badge. Open the action tab of the repository, and select a workflow and click on the Copy status badge Markdown button and add to the README.md file.